This deployment implements a gateway with openwrt running in a virtual machine. So you can run WFilter in the host computer to monitor client computers.
In case you don’t have a mirroring device, you can use this deployment instead. It’s also powerful and reliable.
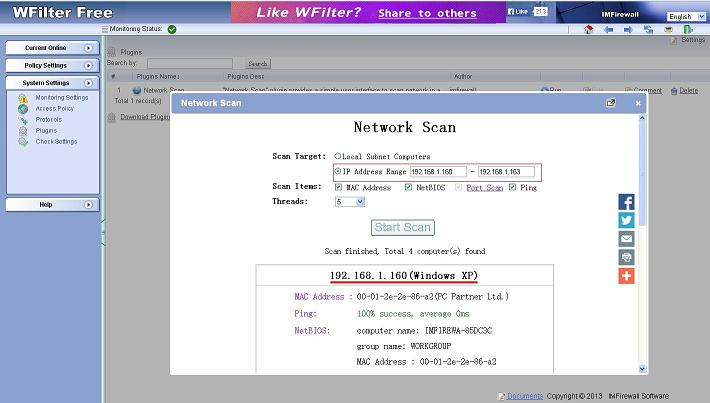
1. Network Topology
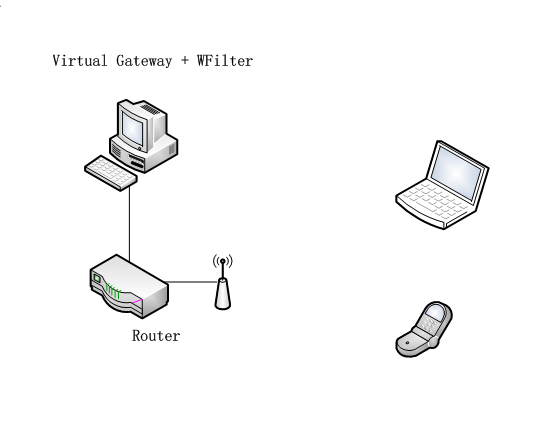
The virtual openwrt gateway is connected to original gateway by a cable. It serves a new subnet to client devices.
2. Steps to build the openwrt virtual gateway.
The host PC runs a windows system and shall be connected with a wired network card.
1). Download and install VirtualBox
Download URL: https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
2). Download the pre-built openwrt vm.
Download URL: openwrt for wfilter
Uncompress it to a local directory, double click file “openwrt_1.vbox”
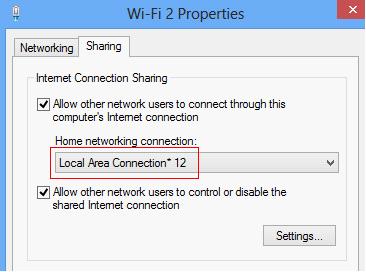
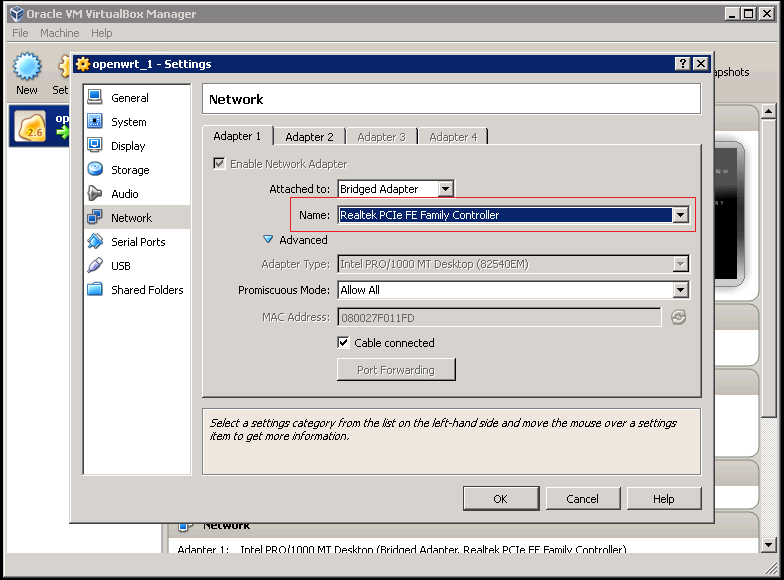
You need to modify the “network settings” of this vm, change “Adapter 1″ and “Adapter 2″ to the network card which is connected to your current gateway.
Now you can start the openwrt vm.

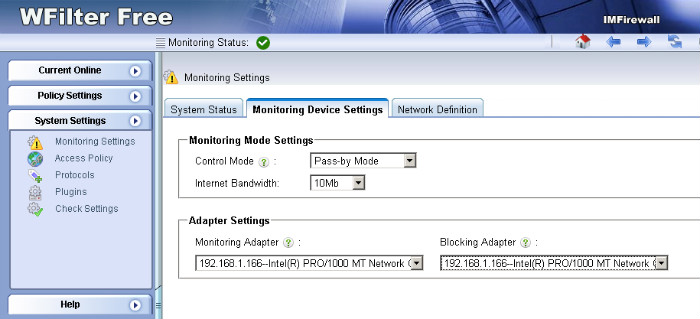
3). Launch openwrt web UI
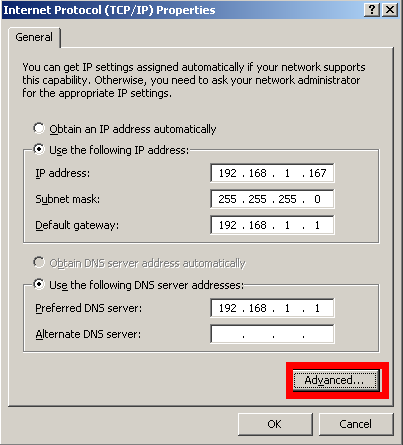
The vm is assigned with a default ip address “192.168.151.1″, to access its web UI, you need to add a 192.168.151.100 ip address to your current adapter.
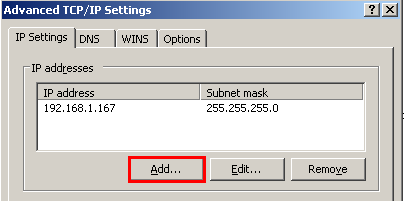
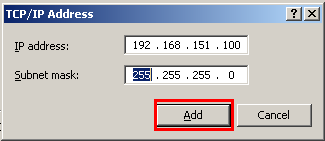
Now you can access openwrt web UI in your browser, from url http://192.168.151.1
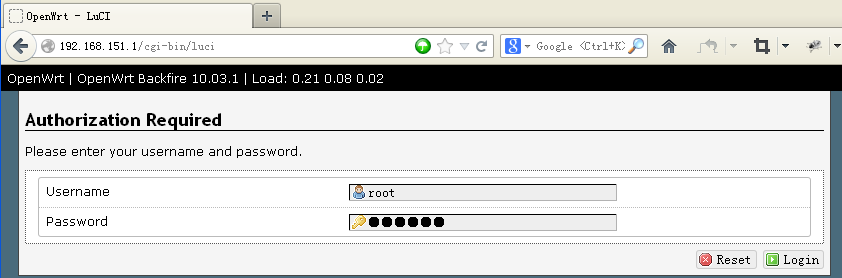
Username is root, default password is: im1234
4). Configure Wan Interface
You can configure wan interface in “Network”->”Interfaces”->”BR”.
The default Wan ip address is “1.1.1.1″, you need to modify it according to your network settings.
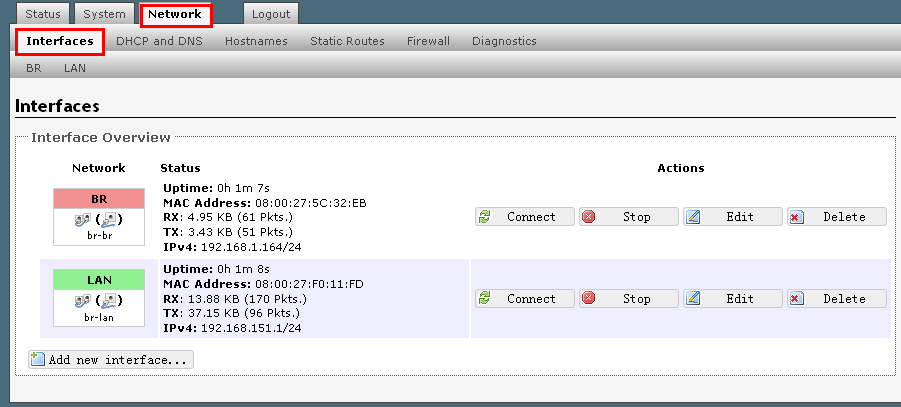
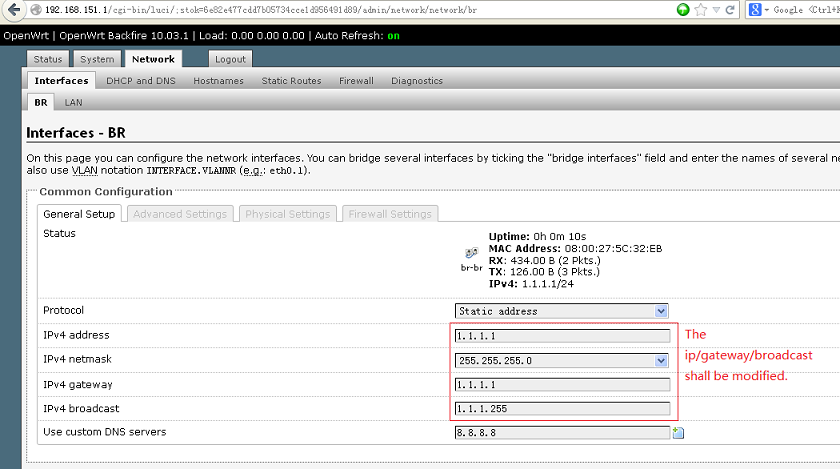
Assign a valid ip address and the gateway ip address to the wan interface.
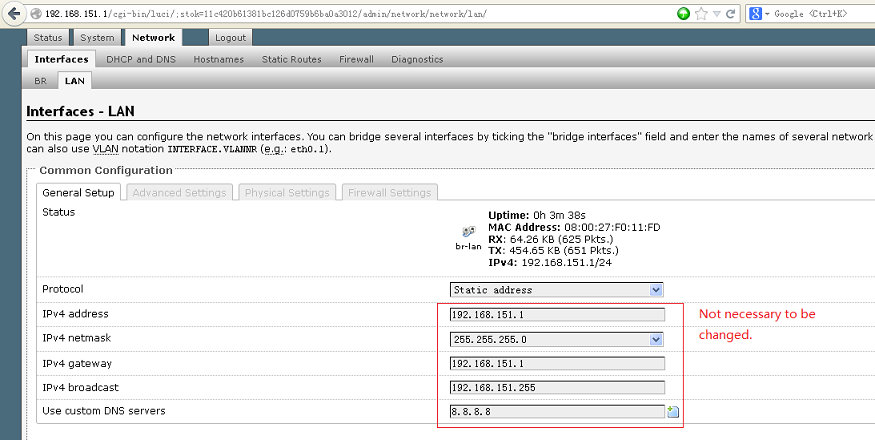
4). Configure Lan Interface
You don’t have to modify the lan interface settings, unless you want to change the default subnet “192.168.151.0″.
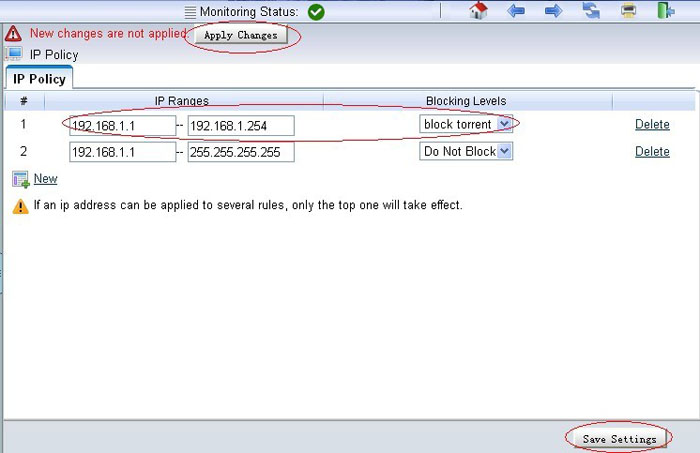
3. Disable DHCP in current gateway
The existing dhcp server(usually the gateway) shall be disabled.
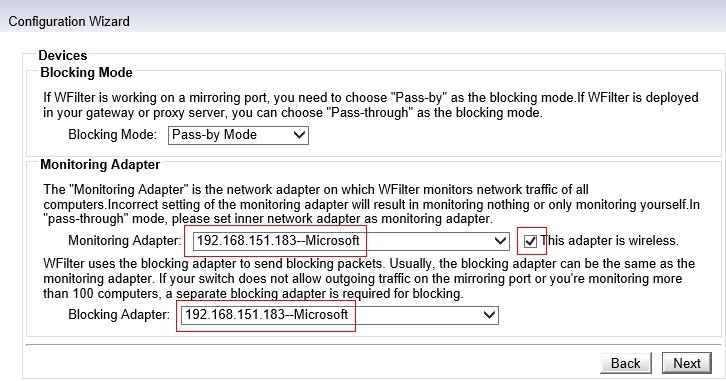
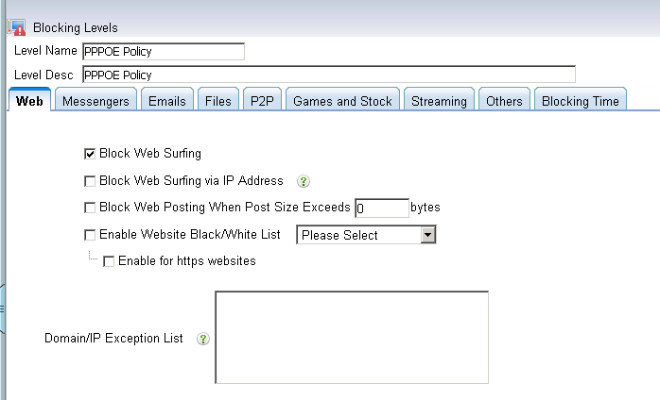
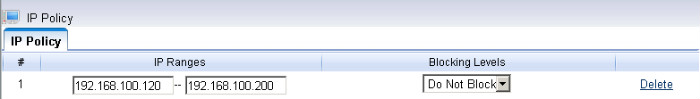
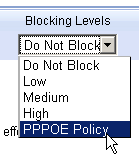
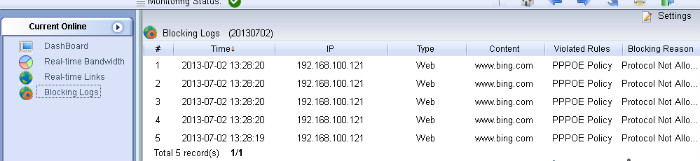
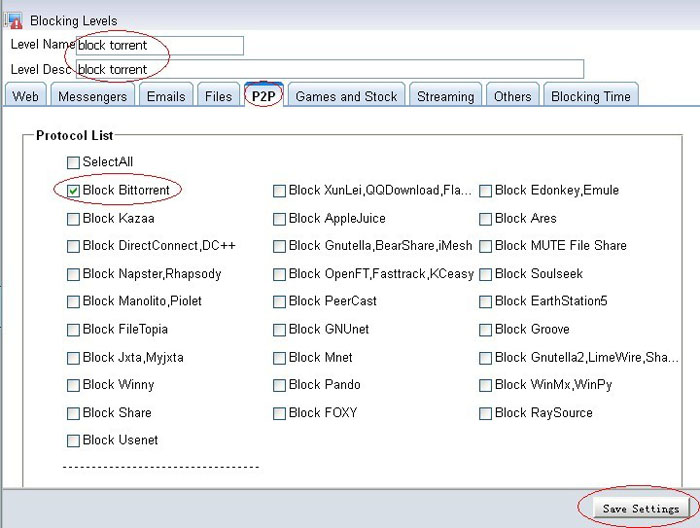
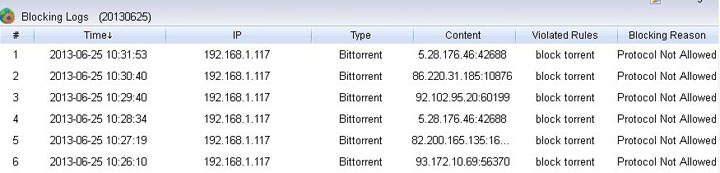
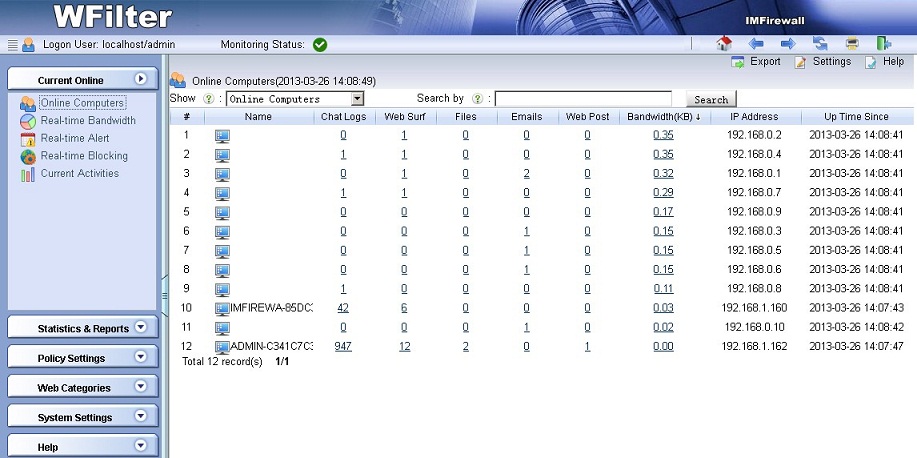
4. Setup WFilter.
Now the virtual gateway is acting as a gateway and dhcp server in your network. Devices obtain ip addresses from this virtual gateway can be monitored in WFilter.